Global & Routine Tests
Highlight coagulation cascade’s dysfunction
PT explores the coagulation extrinsic pathway and can be used for investigating some congenital or acquired bleeding disorders, liver diseases, vitamin K deficiency and vitamin K antagonists therapy.
It allows exploration of so-called vitamin K dependent coagulation factors.
This is the most widely used coagulation assay for laboratory monitoring of anticoagulant therapy with Vitamin K Antagonists (VKA).
* cf Dedicated instructions for use
-
(h)PT-Phen™
Determination of prothrombin time (PT).
Reference Registration Presentation CK581 CE-IVD 12 x 4 mL CK582 CE-IVD 12 x 8 mL CK583 CE-IVD 12 x 18mL 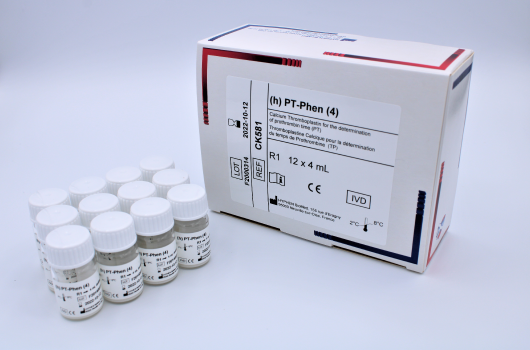
-
PT-Phen™ LRTLiquid and Ready to use
Determination of prothrombin time (PT).
Reference Registration Presentation CK584K CE-IVD 6 x 5 mL CK584L CE-IVD 12 x 5 mL CK586K CE-IVD 6 x 20 mL CK586L CE-IVD 12 x 20 mL 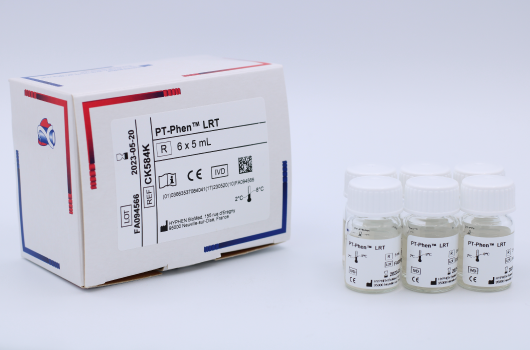
Explores the intrinsic pathway of coagulation and is a screening test to investigate some congenital or acquired deficiencies, especially hemophilia A and B, or coagulation inhibitors such as Lupus Anticoagulant (LA) or autoantibodies against coagulation factors.
* cf Dedicated instructions for use
-
CEPHEN™Liquid aPTT Ready to use
Determination of aPTT.
Reference Registration Presentation CK511K CE-IVD 6 x 1 mL CK512K CE-IVD 6 x 2.5 mL CK515K CE-IVD 8 x 5 mL CK515L CE-IVD 12 x 5 mL 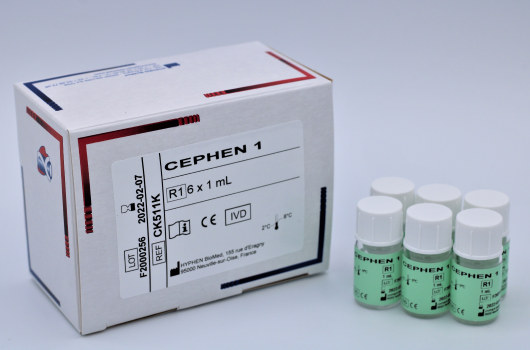
-
CEPHEN™ LSLiquid aPTT Lupus sensitive Ready to use
Determination of aPTT.
This reagent offers a good sensitivity to the presence of LA.Reference Registration Presentation CK521K CE-IVD 6 x 1 mL CK522K CE-IVD 6 x 2.5 mL 
Elevated fibrinogen concentrations are observed in inflammation and have also been considered as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and thrombosis.
Hypofibrinogenemia can be present in patients with fibrinogen deficiency or dysfunction (abnormal protein), and is also associated with severe liver diseases, or excessive consumption (Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)).
Numerous variants of fibrinogen have been described, and are associated to asymptomatic cases or hypofibrinogenemia, with clinical manifestations of bleeding, or thrombosis (resulting from an impaired fibrinolysis).
* cf Dedicated instructions for use
-
FIBRIPHEN™ LRTLiquid and Ready to use
Measurement of the fibrinogen concentration in plasma using the von Clauss method. This reagent is available with the lyophilized presentation, or the ready to use liquid format.
Reference Registration Presentation CK585K CE-IVD 6 x 5 mL 
-
FIBRIPHEN™
Measurement of the fibrinogen concentration in plasma using the von Clauss method. This reagent is available with the lyophilized presentation, or the ready to use liquid format.
Reference Registration Presentation CK571K CE-IVD 6 x 1 mL CK572K CE-IVD 6 x 2 mL CK575K CE-IVD 8 x 5 mL 
-
LIAPHEN™ FibrinogenLiquid and Ready to use
Determination of Fibrinogen antigen (Fib:Ag) in human citrated plasma or in purified medium, using a latex turbidimetric assay.
Reference Registration Presentation 120102 CE-IVD 4 x 5 mL 
-
ZYMUTEST™ Fibrinogen
Measurement of human Fibrinogen in plasma, with an Elisa method.
Reference Registration Presentation RK024A RUO 96 tests 
TT is a screening test to assess abnormalities of fibrinogen and to detect thrombin inhibitors. It can be useful for the exploration of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) and liver diseases.
A prolonged TT can result from the presence of antithrombin activity induced by therapy (e.g. Heparin, Bivalirudin, Argatroban, Dabigatran), the presence of high concentrations of Fibrin/Fibrinogen degradation products or qualitative (dysfibrinogenemia) or quantitative abnormalities of Fibrinogen (deficiency, DIC, fibrinolysis, hepatic disorders including cirrhosis).
TT is normal in presence of a Factor XIII deficiency.
* cf Dedicated instructions for use
-
HEMOCLOT™ Thrombin Time LRTLiquid and Ready to use
Determination of TT in human citrated plasma.
Reference Registration Presentation CK012K CE-IVD 6 x 5 mL 
-
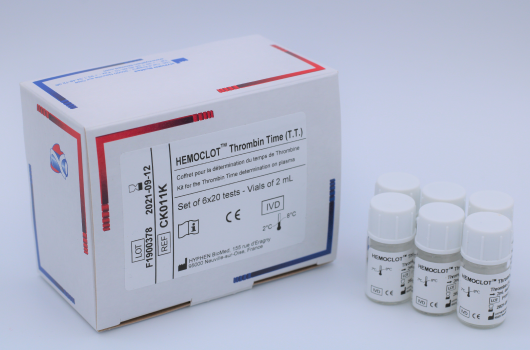
HEMOCLOT™ Thrombin Time (T.T.)
Determination of TT in human citrated plasma.
Reference Registration Presentation CK011K CE-IVD 6 x 2 mL CK011L CE-IVD 6 x 8 mL